
Listen to this post as a podcast:
Sponsored by Peergrade and 3Doodler
Let’s talk about note-taking. Every day, in classrooms all over the world, students are taking notes. I have my own half-baked ideas about what makes one approach better than another, and I’m sure you do too. But if we’re going to call ourselves professionals, we need to know what the research says, yes?
So I’ve combed through about three decades’ worth of research, and I’m going to tell you what it says about best practices in note-taking. Although this is not an exhaustive summary, it hits on some of the most frequently debated questions on the subject.
This information is going to be useful for any subject area—I found some really good stuff that would be especially useful for STEM teachers or anyone who does heavy work with calculations, diagrams, and other technical illustrations. Of course, there’s plenty here for teachers of social studies, English, and the humanities as well, so everyone sit tight because you’ll probably come away with something you can apply to your classroom.
First, Let’s Talk About Lectures
When we think about note-taking, it’s natural to assume a context of lecture-based lessons. And yes, that is one common scenario when a student is likely to take notes. But other learning experiences also lend themselves to note-taking: Watching videos in a flipped or blended environment, reading assigned textbook chapters or handouts, doing research for a project, and going on field trips can all be opportunities for taking notes.
So instead of referring to lectures in this overview, I’ll just talk about learning experiences or intake sessions—times when students are absorbing content or skills through some sort of medium, as opposed to purely applying that content or synthesizing it into some kind of product. Even in student-centered, project-driven classrooms where students pursue their own authentic tasks like the Apollo School, or in more traditional classrooms that set aside time for Genius Hour projects, students need to gather, encode, and store information, so note-taking would still be a fit.
What the Research Says About Note-Taking
1. Note-taking matters.
Whether it’s taking notes from lectures (Kiewra, 2002) or from reading (Rahmani & Sadeghi, 2011; Chang & Ku, 2014), note-taking has been shown to improve student learning. In other words, if we want our students to remember more of what they learn in our classes, it’s better to have them take notes than it is to not have them take notes.
The thinking behind this is that note-taking requires effort. Rather than passively taking information in, the act of encoding the information into words or pictures forms new pathways in the brain, which stores it more firmly in long-term memory. On top of that, having the information stored in a new place gives students the opportunity to revisit it later and reinforce the learning that happened the first time around.
So if you’re not currently having students take notes in your class, consider adding note-taking to your regular classroom routine. With that said, a number of other factors can influence the potency of a student’s note-taking, and that is what these other points will address.
2. More is better.
Although students are often encouraged to keep notes brief, it turns out that in general, the more notes students take, the more information they tend to remember later. The quantity of notes is directly related to how much information students retain (Nye, Crooks, Powley, & Tripp, 1984).
This would be useful to share with students. If they know that more complete notes will result in better learning, they may be more likely to record additional information in their notes, rather than striving for brevity.
Obviously, some students are going to be faster note-takers than others, and this will allow them to take more complete notes. But you can do quite a bit to help all students get more information into their notes, regardless of their natural speed, and that’s what we’ll talk about next.
3. Explicitly teaching note-taking strategies can make a difference.
Although some students seem to have an intuitive sense for what notes to record, for everyone else, getting trained in specific note-taking strategies can significantly improve the quality of notes and the amount of material they remember later. (Boyle, 2013; Rahmani & Sadeghi, 2011; Robin, Foxx, Martello, & Archable, 1977). This is especially true for students with learning disabilities.
One frequently used note-taking system is Cornell Notes. This approach has been around for decades, and the format provides a simple way to take “live” notes in class and condense and review them later.
4. Adding visuals boosts the power of notes.
Compared with writing alone, adding drawings to notes to represent concepts, terms, and relationships has a significant effect on memory and learning (Wammes, Meade, & Fernandes, 2016).
The growing popularity of sketchnoting in recent years suggests that teachers are well on their way to taking advantage of this research.
This video combines sketchnoting with Cornell Notes, and it’s an approach I think is definitely worth considering.
To explore sketchnoting more deeply, check out this list of sketchnoting resources compiled by celebrated education sketchnote artist Sylvia Duckworth.
5. Revision, collaboration, and pausing boosts the power of notes.
When students are given the opportunity to revise, add to, or rewrite their notes, they tend to retain more information. And when that revision happens during deliberate pauses in a lecture or other learning experience, students remember the information better and take better notes than if the revision happens after the learning experience is over. Finally, if students collaborate on this revision with partners, they record even more complete notes and score higher on post-tests (Luo, Kiewra, & Samuelson, 2016).
With this in mind, it would be a good idea to plan breaks in lectures, videos, or independent reading periods to allow students to look over, add to, and revise their notes, ideally with a partner or small group. This partner work could happen after students have had time to revise their notes alone, or students might be given access to classmates for the duration of the pause.
6. Scaffolding increases retention.
Teachers can build scaffolds into their instruction to ensure that students take better notes. One very effective type of scaffold is guided notes (also called skeleton or skeletal notes). With guided notes, the instructor provides some type of outline of the material to be covered, but with space left for students to complete key information. This strategy has been shown to substantially increase student achievement across all grade levels (elementary through college) and with students who present with various disabilities (Haydon, Mancil, Kroeger, McLeskey, & Lin, 2011).
As instructors experiment with guided notes, certain features show a lot of promise. One that I found incredibly interesting was a style developed by engineering professor Susan Reynolds to accompany her lectures: The notes combine typed information, handwritten content, and graphics, but still leave room for student notes and working out example problems.
Diagrams are pre-drawn, but some key numbers are left out for students to fill in during the lecture. These notes consolidate all the technical material for a lecture into a single document, and the information is organized to align with the lecture. The more I study these notes, the more I see how useful they are, and how well they balance the efficiency offered by guided notes with the need for students to actively participate in the encoding process.
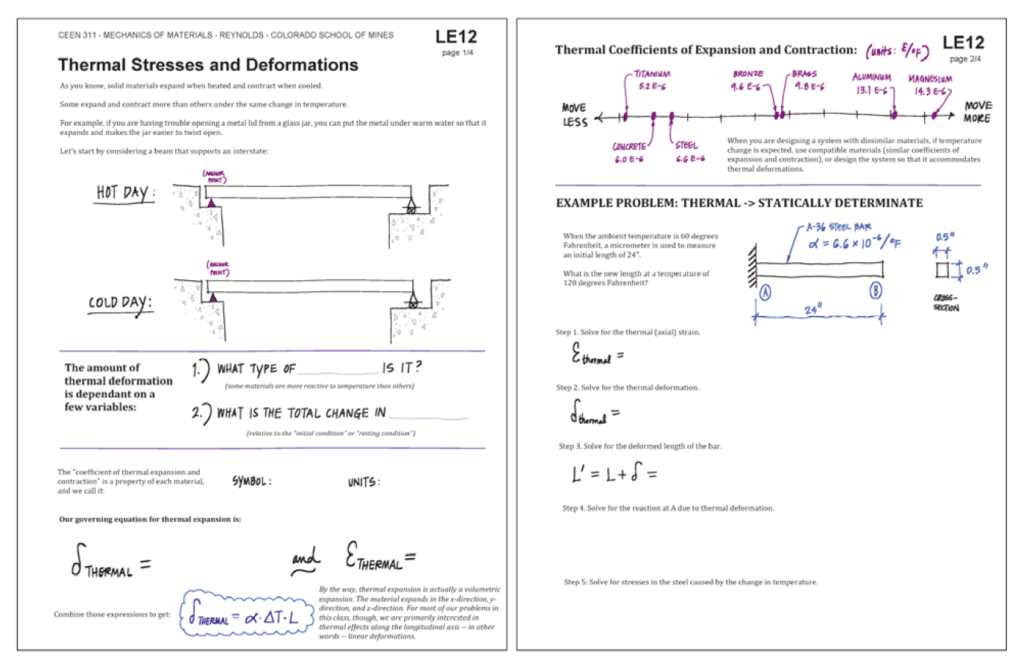
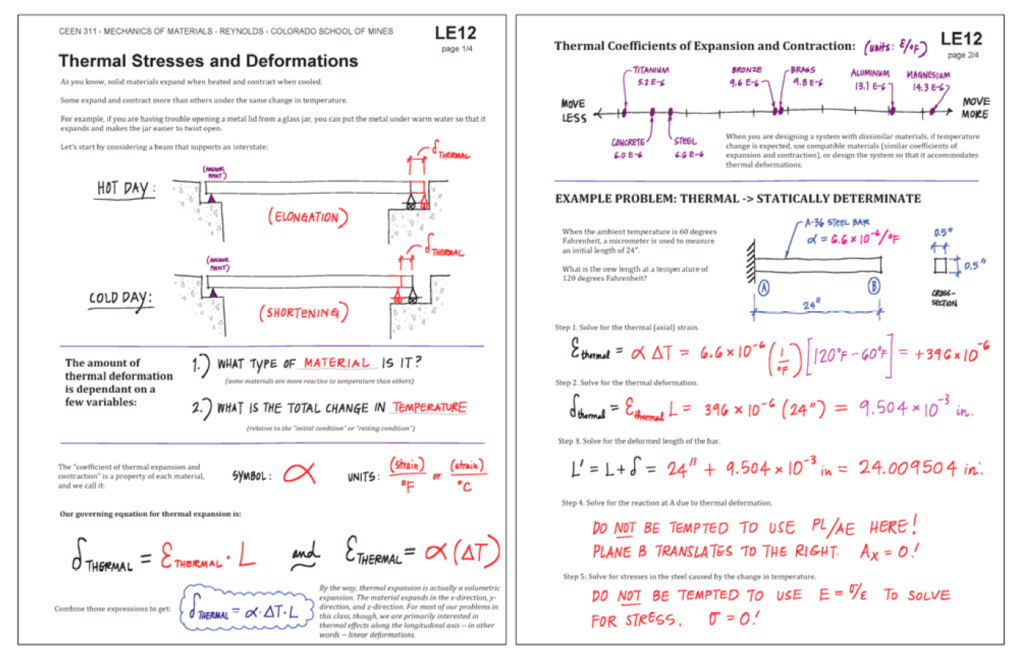
Reynolds’ students have had strong positive reactions to this style of notes and consistently attribute the notes as a key factor in their engagement and learning in the course (Reynolds & Tackie, 2016).
While teachers should experiment with different styles, the take-away here is that if you want students to get the most out of a learning experience, provide them with some form of partially completed notes.
In the meantime, you can add another layer of scaffolding by simply adding more verbal cues to your learning experiences (Kiewra, 2002). Research shows that simply saying things like, “This is an important point,” or “Be sure to add this to your notes,” instructors can ensure that students include key ideas in their notes. Providing written cues on the board or a slideshow can also help students structure their notes and decide what information to include.
7. Providing instructor notes improves learning.
In an article I wrote a few years ago, I denounced instructor-prepared notes as an ineffective method for teaching, primarily because encoding this information required no effort from students and therefore made the learning too passive.
Although I stand by the assertion that we should avoid simply supplying students with notes, I need to refine the message: Research has shown that when we give students complete, well-written, instructor-prepared notes to review after they take their own notes, they learn significantly more than with their own notes alone (Kiewra, 1985).
If we combine this strategy with student revision, collaboration, and pausing to improve note-taking and learning—in other words, having students pause during an intake session to collaboratively revise their notes, then let them review instructor notes at the end—we can give our students an incredibly powerful learning experience.
One concern is that providing notes might make students more passive about taking their own notes during the learning experience. Here are some suggestions for addressing that:
- Assigning a small grade for student notes would likely compel most students to do them, but this could distort the validity of a grade, as we discussed in another post.
- It would probably be more effective to simply build note-taking into the class activities. For example, if students are encouraged to take notes, and then they are given a pause every few minutes to compare and revise notes, it would be pretty awkward for them to turn to a partner and have nothing to contribute.
- Sharing the research with students that those taking notes then revising them with instructor notes has greater impact than instructor notes alone might push students to take more notes.
- Allowing students to choose a note-taking format that works best for them would also boost student motivation for taking the notes.
8. Handwritten notes may be more powerful than digital notes, but digital note-taking can be fine-tuned.
Studies have shown that students who take notes by hand learn more than those who take notes on a laptop (Mueller & Oppenheimer, 2014; Carter, Greenberg, & Walker, 2017).
This research confirms what a number of educators suspect about the negative effects of digital devices in the classroom, and some have taken it to mean they should definitely ban laptops from their lectures (Dynarski, 2017). Others argue that prohibiting laptop use robs students of the opportunity to develop metacognitive awareness of their own levels of distraction and make the appropriate adjustments (Holland, 2017).
Because technology is always changing, and because as a species, we are still adjusting to these new formats, I would hesitate to ban laptops from the classroom. Here’s why:
- Research on this topic is still pretty young: Some researchers have found no significant difference in performance between paper-based and digital note-takers (Artz, Johnson, Robson, & Taengnoi, 2017). My guess is that more research will pile up and get more refined, so we should take a measured approach for the time being.
- Other researchers are looking at ways to reduce some of the problems associated with digital note-taking, like distraction: One study found that while doing online research, students who used matrix-style notes and were given time limits were much less likely to become distracted by other online material than students without those conditions (Wu, & Xie, 2018).
- I believe we serve our students better by helping them find a note-taking system that works best for them. With that in mind, I would be more likely to have students experiment with hand-written and digital notes, share the research with them, and give them opportunities to reflect on and measure their results.
See What Other Teachers are Doing
To learn more about what other teachers have found to be most effective note-taking methods, I put the call out on Twitter, asking teachers to share what works for them. You can browse that conversation here.
References
Artz, B., Johnson, M., Robson, D., & Taengnoi, S. (2017). Note-taking in the digital age: Evidence from classroom random control trials. http://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3036455
Boyle, J. R. (2013). Strategic note-taking for inclusive middle school science classrooms. Remedial and Special Education, 34(2), 78-90. https://doi.org/10.1177%2F0741932511410862
Carter, S. P., Greenberg, K., & Walker, M. S. (2017). The impact of computer usage on academic performance: Evidence from a randomized trial at the United States Military Academy. Economics of Education Review, 56, 118-132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2016.12.005
Chang, W., & Ku, Y. (2014). The effects of note-taking skills instruction on elementary students’ reading. The Journal of Educational Research, 108(4), 278–291. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2014.886175
Dynarski, S. (2017). For Note Taking, Low-Tech is Often Best. Retrieved from https://www.gse.harvard.edu/news/uk/17/08/note-taking-low-tech-often-best
Haydon, T., Mancil, G.R., Kroeger, S.D., McLeskey, J., & Lin, W.J. (2011). A review of the effectiveness of guided notes for students who struggle learning academic content. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 55(4), 226-231. http://doi.org/10.1080/1045988X.2010.548415
Holland, B. (2017). Note taking editorials – groundhog day all over again. Retrieved from http://brholland.com/note-taking-editorials-groundhog-day-all-over-again/
Kiewra, K.A. (1985). Providing the instructor’s notes: an effective addition to student notetaking. Educational Psychologist, 20(1), 33-39. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep2001_5
Kiewra, K.A. (2002). How classroom teachers can help students learn and teach them how to learn. Theory into Practice, 41(2), 71-80. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip4102_3
Luo, L., Kiewra, K.A. & Samuelson, L. (2016). Revising lecture notes: how revision, pauses, and partners affect note taking and achievement. Instructional Science, 44(1). 45-67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-016-9370-4
Mueller, P.A., & Oppenheimer, D.M. (2014). The pen is mightier than the keyboard: Advantages of longhand over laptop note taking. Psychological Science, 25(6), 1159-1168. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797614524581
Nye, P.A., Crooks, T.J., Powley, M., & Tripp, G. (1984). Student note-taking related to university examination performance. Higher Education, 13(1), 85-97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00136532
Rahmani, M., & Sadeghi, K. (2011). Effects of note-taking training on reading comprehension and recall. The Reading Matrix, 11(2). Retrieved from https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/85a8/f016516e61de663ac9413d9bec58fa07bccd.pdf
Reynolds, S.M., & Tackie, R.N. (2016). A novel approach to skeleton-note instruction in large engineering courses: Unified and concise handouts that are fun and colorful. American Society for Engineering Education Annual Conference & Exposition, New Orleans, LA, June 26-29, 2016. Retrieved from https://www.asee.org/public/conferences/64/papers/15115/view
Robin, A., Foxx, R. M., Martello, J., & Archable, C. (1977). Teaching note-taking skills to underachieving college students. The Journal of Educational Research, 71(2), 81-85. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1977.10885042
Wammes, J.D., Meade, M.E., & Fernandes, M.A. (2016). The drawing effect: Evidence for reliable and robust memory benefits in free recall. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 69(9). http://doi.org/10.1080/17470218.2015.1094494
Wu, J. Y., & Xie, C. (2018). Using time pressure and note-taking to prevent digital distraction behavior and enhance online search performance: Perspectives from the load theory of attention and cognitive control. Computers in Human Behavior, 88, 244-254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.07.008
Join my mailing list and get weekly tips, tools, and inspiration that will make your teaching more effective and fun. You’ll get access to our members-only library of free downloads, including 20 Ways to Cut Your Grading Time in Half, the e-booklet that has helped thousands of teachers save time on grading. Over 50,000 teachers have already joined—come on in.




What grade should note taking begin? Middle school? Upper elementary? 🤔🤔
I have the same question. I teach gr 3 and am trying to think of ways to incorporate this into our class.
And THANK-YOU for consolidating all the research for us here! This website is my go-to source for research-backed, teaching best-practice info.
I’ve done some of this in grade 3! For example, we watched a video and I asked them to jot down what they noticed. We’d recently done some mind mapping so I suggested they do it in that format. Then I asked them to share what they had noticed and we made a mind map together, with students adding anything they had missed (wherever they felt it fit best).
Hi, Joyous! I love that you’re asking this question. What about 1st grade? Kids love to write and doodle, right? As a former 1st grade teacher, all throughout the day, I provided tons of opportunities for kids to record their thinking. They were writing, doodling, drawing arrows, labeling, captioning … doing all that stuff that we want them to do when showing understanding. Of course, this came with a lot of scaffolding, modeling, and direct teaching. I think sketchnoting is perhaps the most natural way to get kids started. Here’s a specific activity I did at the end of the year that some might say was a science lesson, others a reading lesson, and others a writing lesson. I say it was all that and more. My real intention was to teach a learning process: 1. Listen to just get familiar with the content. 2. Listen again, this time really visualizing the content. Draw, write, label what you understand. 3. Listen again and fix or change. The tool we used was a Scholastic News issue that happened to coincide with our weather unit. (I read it aloud, one section at a time.) Here’s a link to 4 samples of student work. In case you’re wondering, one of the samples is from an ELL student, another from a struggling student and another from a gifted student. Several note-taking strategies were part of this lesson: sketchnoting, revision, pausing, scaffolding, and shout-outs, which I considered a form of collaboration. While kids were sketching and revising, I saw some really neat things happening, that I’d just shout out. For example, “Hey, if anybody’s interested, I’m noticing Johnny is numbering the different stages. See if that’s something that will work for you.” I’ll be honest. I did this lesson 3 years ago and at the time, I didn’t even think of it as notetaking. Then Jenn’s post helped me realize that note-taking, that thing I hated most growing up (almost as much as I hated liver and onions for dinner) was actually something I was teaching my 1st graders. Not only could they do it, but they enjoyed it…and the learning really did stick. Hope this helps!
I think note taking should start in middle school.
note taking should begin at the earliest time possible. If there is time in elementary school then good. Does vocabulary count as note taking. I mean remembering how to spell is important.
kindergarten
I think note taking should start from elementary.
Thank you for consolidating the research. You’ve given me a lot to think about.
This:
“Whether it’s taking notes from lectures (Kiewra, 2002) or from reading (Rahmani & Sadeghi, 2011; Chang & Ku, 2014), note-taking has been shown to improve student learning. In other words, if we want our students to remember more of what they learn in our classes, it’s better to have them take notes than it is to not have them take notes.”
Does it improve student “learning” or “retention”? I think there is definitely power in taking notes but does this actually look at deep understanding of a concept and application or retention and regurgitation? Would love to know your thoughts.
Thanks for sharing this! So much great stuff 🙂
Hey George,
I think we can define “learning” in a lot of different ways. If students are only consuming information, recording it, and then regurgitating it, but never applying it in any authentic way, then it’s questionable whether they are really learning it.
On the other hand, without consuming actual information and ideas that have been put out into the world by others, students will be limited in how far their application can go. I can think of all kinds of examples, but I’ll use myself here:
When I wanted to create a podcast, I watched a lot of YouTube videos and read a lot of articles that taught me how to do it. I took notes. Lots of them. Messy at first, but then I rewrote and reorganized them so they were more useful to me later. I watched some of the videos more than once and revised my notes. Then, as I practiced with all the technical elements of audio recording and editing, I referred back to those notes. The learning was an interplay between intake, processing (note-taking), and application. If any of those parts were missing, I think the learning would suffer.
Thank you for the useful information!
Loved this. I’ve been trying to wrap my head around how to teach my kids with special needs how to do notes, and I loved how you covered scaffolded notes and the digital issue. This is just amazing.
I saw Daniel Willingham, a widely respected educational researcher, present on this topic a year or so ago. This post by him is a good summary and also points to some research studies that you didn’t include. Enjoy, everyone! https://tinyurl.com/ycxtk4rf
Thanks so much, Angela!
A very important issue in note taking is the distinction learning from taking notes and using notes to learn. These processes are distinct and very different issues can be important with each. If notes are not used for review, some learners would be better off note taking notes. Note review does not necessarily depend on the learner taking notes.
What a great resource on how to make note-taking an integral part of our classroom. I am planning on using a few TED talk videos in my 9th and 11th grade English classes, and this has helped me think about how to have the students taking notes in a much more scaffolded way for their learning.
Thank you, Jennifer, for such a useful and thoughtful post. I’ve just translated it to Portuguese to share with my colleagues and oldest students at my school.
Your writings have already inspired my teaching so many times!
Ines
Thank you for that wonderful summary. I was looking for ways to introduce note-taking for my fourth graders. This gave me tons of info. Thank you 😊
Great post!
I’m wondering if you have any handy-dandy “how to take notes” mini-courses like the plagiarism one you created? I bought that one and love it! Thanks for all of your hard work and your honesty. It shines through in your podcasts.
I have been thinking about doing one…It’s just not made yet!
I’ve used Cornell notetaking for many years now. And I’ve added a column on the right to place visuals. And like Doug Neill, I’ve observed some of my high school students using the visuals on their tests! I’ve given them extra points for using them. I’m excited to use more visuals this year!Great info. Thanks
The age-old tradition of note-taking with a few more research based findings made this podcast truly interesting, and for that, Jenn needs to be complimented for preparing and sharing such an important part of learning at all academic levels. As a high school teacher of 30+ years, I have always encouraged my students to take notes at all time, having a notebook open and ready to go- write, draw, doodle, something. I do give them ideas on how to be a great note-taker! I kept my hand-written notes for years (depending on my need for them in high school, undergraduate, and then graduate school) I even have years of notes as a teacher and I always feel that adding or editing newer versions has been fun and has brought new meaning to teaching. With changes coming along with 21st-century learning, it is always good to blend the old and the new… thank you Jenn for bringing new light to this tradition. Cheers.
Hi Jennifer,
Thank you so much for sharing your finds. I am curious to hear your thoughts about taking notes in a proficiency/ci based world language classroom. I provide the students with visuals and specific phrases in context for comprehension purposes. I have strayed away from traditional practices in the language classroom, and therefore having the students sit for 20-25 minutes taking notes is not a reality in my classroom.
Thanks!
Kia
Hi Kia ~ I’m not familiar with the methods you’re describing. I found something about Comprehensible Input in language learning, but I’m not sure if that’s right. Also, the description I read didn’t make much sense. If you could explain the process a bit more, that would help.
With that said, what I’m trying to get across in this post is about the value of note-taking in general, and in some classrooms, that might mean just a few notes every couple of days. It wouldn’t have to be 20-25 minutes of solid note-taking. In your class, do students take in any information that they might remember better by writing it down? If so, and if they don’t currently have any strategies for doing that, you might consider building it into your class time.
I love the information on scaffolding and guided notes! I see so much value and potential in that to help kids get the value of note taking even if thier natural aptitude is poor in this area.
Do you have any suggestions on how students who struggle with note taking like my daughter who is dyslexic, as well as been diagnosed with DCD (developmental coordination disorder) can modify note taking so they can gain the benefit of the process without using all available focus and attention on it, and losing out on the greater information because they are struggling with writing and spelling?
Hi Angela ~
I have a couple of suggestions: (1) Guided notes are especially helpful for students who don’t take notes quickly. If her teachers are willing/able to provide skeletal notes where more is already written down and your daughter just fills in key information, it would really benefit her. (2) She could be paired with another student in class who takes good notes and sit beside that student, watching as the notes are built and even suggesting additions or changes as they are written. Then the notes could be copied (or shared digitally) for your daughter to use in her own studies. (3) She could make audio recordings of lectures and listen later so she can add to the notes she took during class. Using something like a Livescribe Pen would even tie her written notes in with specific parts of the audio.
This collection looks like it would have some more in-depth suggestions.
Hope this helps!
Thanks so much for this, already shared with all my HS classes with appropriate emphasis of course. I find assigning a simple grade that is reviewed regularly helps with motivation 1-3 dependent on the level of engagement/reflection.
On the point of handwritten v typed notes, I’m so tired of hearing this argument trotted out, a close reading of the research shows that the issue is not the medium, but the method; ie are they mindlessly transcribing, or actively summarising/reflecting/questioning? When taught the latter, then the medium used is irrelevant, the bigger issue—as your post so effectively highlights—is that note taking is rarely actually taught (like the skill of summarising and paraphrasing) it’s assumed that it’s an automatic talent… For those that are interested in a more critical consideration of the research around typing and note taking, please see my post here: http://doverdlc.blogspot.com/2016/04/typing-vs-writing.html
Thanks for sharing this, Sean.
Just an update for you. In the months since we revisited note taking with renewed vigour inspired by your article, it’s been reassuring to see how effective this practice is. But I have to say my thoughts in handwritten v digital have deepened as a result… I LOVE the wise/nuanced position you take in this post, but FWIW, here’s what I’m noticing with my HS students, who all use digital notes:
I’m a ‘tech coach’ and developed a model I call SAMMS to facilitate ways to help teachers move their use of digital tools from replacement to transformative (RAT) or Substitution to Transformation (SAMR). Applying that model to note taking, looks like this :
Notes that are situated: read, update, edit from anywhere, any device, any time, any place that suits you. Very difficult to lose notes this way as well.
Notes that leverage internet access: links to web resources, clarify information, add quotes, definition of terms. Notes are searchable, this alone is a game changer.
Multimodal notes: inclusion of rich media, eg image, video, voice notes…
Notes that are mutable: revisit notes and make edits/updates, especially as your perceptions/understanding evolves over time.
Social: share notes with a partner and peer/pair share. Notes shared with a teacher facilitate accountability, but also the possibility of feedback by the teacher. (This has been amazing, I learn as much from the content of their notes, as I do from any assignment they do, probably more… BTW I do grade these 1-3 just to indicate level of engagement, based on this article in fact, eg more detail, more personal!)
…
So if you exploit SAMMS then digital note taking is a no brainer, but combining strategies works well too, eg take notes by hand, in real time, very short hand, then type/dictate them up and add detail later; this also acts as a great opportunity to reflect, revisit, consolidate.
Hey Sean,
Thanks for taking the time to share this strategy-it seems to be making an impact!
I loved your video. Great ideas I plan to try with my Aspire/GED class. Thank you.
Great to hear, Paul! I’ll be sure Jenn sees this.
Thanks for this great post & reminder. I was just needing to add formal textbook kind of learning to what students learned in a hands-on lab. Using some of your points, I hand-drew an interactive notetaking guide to the chapter that might have resembled a treasure hunt more than note-taking. After using it with 8th graders the past 2 days, I can tell you that it was more effective.
I did a little variation on the pause/reflect step. I had them do that and then collected and redistributed all the papers. Everyone had a someone else’s paper. They read thru the paper and concentrated on their recap summaries. We talked about what they noticed, what was good & what could be improved. THEN we talked about how a coach tells players how to improve on something without being “mean”. They wrote a note for improvement on the paper and briefly explained it.
And then each person got their original paper back…decided how much of the suggested improvement was valid and I gave them time to make an improvement. Especially encouraging them to make a judgment about whether the suggestion was worthy of doing or if they could customize it even better.
I will tell you that between the highlighters, colored pencils, recaps, suggestions for improvements and class pauses (which I call Hey Wait a Minutes)….it went 1,000,000% better.
Thanks for your suggestions and good ideas.
Yay! This is great to hear — thank for sharing, Marsha!
Wow — so much good stuff here. I bet your students loved it, too. Thanks for sharing this!
Do you have an example of this? This sounds engaging.
This podcast couldn’t have come at a better time. Starting next week, I’m attempting a note-taking portfolio for the semester that I’m really excited about.
I teach ESL to international students at a university. We’ve done listening/note-taking practice with pre-recorded lectures and an open-notes comprehension test at the end, but its inauthenticity has always driven me crazy.
So, I made my students buy Rocketbook Everlast notebooks and Frixion Pens (not an ad, I promise) in lieu of a textbook. They will have to have take notes in their major grad/undergrad classes, then submit compile their notes into a .pdf – easy to do with these notebooks – and submit them weekly/biweekly. I’ll be giving small amounts of feedback and adding criteria based on different learning theory (ex: try dual coding/sketchnotes, or Cornell notes, etc…). My hope is that this will create buy-in and accountability, while also helping them by successful in their other class. Fingers-crossed!
Thank you for all you do. Even though I’m not your typical audience, your work has been a huge inspiration! A tech-loving, graphic-designing creative who’s serious about innovation and best practices in teaching? It ticks all my boxes. 🙂
Thanks so much for sharing this, Natalie!
I love this task… but it seems a bit long.
I find Handwritting my notes more beneficial, because I can remember what I’ve written, it’s like instant mental picture in my head of words I’ve wrote, or maybe… I don’t know, just maybe I’m too “old school”. 🙂
Hi Jennifer. Thank you so much for this episode. I needed to get a clear idea of research on note taking. That being said I must express that I am frustrated at the results.
I don’t mean any criticism to you for what you’re reporting. Obviously, the results of these studies are in no way a fault of yours. Still, as a student with a learning disability who has struggled with note taking, as a student who is always the one who couldn’t get everything down even with the professors obviously pausing, I have to responsibly challenge these results.
At the same time, I don’t want to deny my bias in this matter because I struggle so hard. I feel like how many of the students I tutor in math must feel when they tell me they are bad at math. In most cases, I use Socratic method to teach them and they prove to me that they are not bad at math at all. I feel a similar disappointment that they feel for being bad at taking notes.
I don’t like notes. I don’t want to have to take notes. I don’t want to even feel pressured to take notes. With that said, I can think of a few scenarios where I would be happy regardless of note taking being a necessary part of a class.
The first scenario that comes to mind is in line with what you mentioned on this episode where teachers give their own notes. But I’m already beginning to stress out just at the thought of those notes being incomplete. The idea that I have to be paying attention at exactly the right moment to hear that one piece of information or else lose it forever is too much pressure.
The second scenario that comes to mind is is what I think could be ideal. If I were teaching class I would have my class connect with me on a single Google doc where I have information already written to some degree as a skeletal structure of what I’m going to teach but I let them collaboratively make a single set of notes together. The real magic of Google Docs isn’t just the collaboration Factor but the option 2 highlight a section of the material and comment with a question that has its own thread that can expand in dialogue with others just to figure out what does this mean?
Those are the real sorts of things that have helped me in my studies. Rather than being spoken at, I benefit from having an open dialogue where I can have a back and forth of asking questions until I understand what the teacher is trying to communicate. Most of my professors and teachers have felt too busy or too rushed to be able to handle the questions that I have. They even tell me that I have great questions but there’s never enough time for them… while the alternative is that there’s never enough time for me.
I’m going to keep reading through your sources and keep commenting and asking questions here so that I can hopefully get an idea of the best way where I can move forward. I appreciate any and all feedback and challenges to my own position that you’re willing to offer.
Steve, it sounds like you are a unique learner – but also that you understand what works best for you. (And what doesn’t.) As a high school teacher, I would recommend 1) Explaining to each teacher/professor what your needs are, and asking for permission to video. You would need to assure them that the video won’t be posted anywhere, or shared with anyone. I think many instructors who understand why you wish to have them will grant that permission, provided you don’t give them any reason to distrust you. 2) As you listen to the live lecture, write down your questions. Go to them after class/during office hours, and address those questions. It’s not that they don’t want to answer your during class, it’s simply a matter of time, as you mentioned. But office hours/after school provide a chance for you to get what you need, and at a pace that is more comfortable. 3) Ask if there is any way that you could get a snapshot of upcoming lectures so you have questions already formulated. So, you if know that next week the lecture is on Chapter 20, read it and send those questions beforehand to the teacher. Hopefully they can address those questions during their lecture, or they can reply to you via email.
I do hope you find what works for you – keep at it!
On the subject of digital note taking, I have found that I can take notes as fast as my classmates if they are text only. The trouble comes first when there’s equations which isn’t so much a problem now because I’ve taught myself latex code to help with that. Then there’s the final problem that I haven’t really solved which is win I need to draw something like a graph. Unfortunately, I don’t have a device that can work with a stylus and everything I’ve tried drawing with a mouse takes too long to keep up with the notes.
One option that sometimes worked is taking pictures in class. I had the OneNote app linking to my notes on it but the software would often lag and be too slow to trust in the moment. If we simply switched to video lectures, I think that I would do a lot better because I can both listen at twice the speed of a normal lecture while also taking my time to write the notes and know that I covered everything that’s important when I’m done with the video. People keep telling me that some teachers let students record them on video but I haven’t met one such teacher yet.
Wow! This is quite interesting.
My take home are:
*Revision, collaboration and pausing boosts the power of notes. I have done this in time past but not intentionally. I understand now how helpful this will be to the learning process.
*Providing Instructor notes improves learning. This was my major focus before now but I would rather have my students put down their understanding first so that misconceptions can be addressed while right concepts are strengthened through collaboration before giving my own notes.
What do you think about pasting the instructor’s note in the student’s notebooks?
When discussing note taking, I find it useful to consider purpose. The classic distinction is the immediate goal of more active process and the long term goal of external storage (for study). This distinction is a great way to analyze issues such as access to distraction and the role of expert notes.
Hi Jennifer,
Thanks for sharing your research on note-taking. I am a secondary teacher in Ontario. The course I teach is called Learning Strategies, which is to help students with “exceptionalities”, such as a Learning Disability or ADHD. I have been doing most of your proposed strategies in my class and you reaffirmed the important need based on research. My students are also in other subject classes and some have an accommodation (often related to grapho motor, processing, attention, or memory issues) for note-taking assistance or to be provided with copies of notes. Even with guided notes, the use of a computer, and copies of slides (provided before or after the lesson) many students struggle or resist trying to take notes. Nevermind revising notes, but the idea of doing it in class is important. Do you have any ideas (articles, contacts, strategies) that might be good for myself and my students to review? I suspect this is also a problem for post-secondary students.
Do you or any of your readers know of workshops (or conferences, or classes, etc.) that I could attend to learn more about teaching good note-taking using some or all of the strategies you address? Thank you in advance for any helpful suggestions you or others share.
Sylvia Duckworth offers some workshops and classes you might want to check out. That’s all I know of right now — hope it helps!
Thank you!
I think that more workshops and classes should be added because we all can learn something from deeper learning and note taking skills.
For years I have been using student centered notes in my class. Students are given a choice of note-taking methods. Examples are guided notes, cornell notes, sketch-notes and digital note-taking. Concept maps are also helpful tools.
Thank you for pointing out that there are multiple studies about notetaking that need to be considered. People don’t seem to notice that the Oppenheimer and Mueller study was done on students at Princeton- the outcomes may not be expected for everyone. Students with disabilities or poor working memory may still need computer access just to take effective notes. How does banning computers in a lecture help students that are differently abled? Here is a study that shows computers can help bridge that gap: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Note-taking-with-computers%3A-Exploring-alternative-Bui-Myerson/0352ed76cb27ff9b0edecfcf9556bc1e19756e9e
I agree with what John said about note taking. I usually do cloze notes but started doing electronic notes this year. seems to be working well for some students
Scaffolding is extremely important for special education students to effectively access the general education curriculum. I believe the same practice for this group of students should be implemented universally for all students.
As a first year teacher, reading about the benefits of guided notes was very reassuring. I teach 8th grade English and have a high percentage of students with special needs and who are English Language Learners. So I started out using guided notes for nearly every time they need to take notes. I adopted the practice with my other students as well, because they seem to benefit as well. I also want to make sure they have all of the information, and they take such a long time to write down everything (even if it’s honestly not that much). I try not to spend a lot of time “lecturing,” but if I’m stopping for upwards of 5 minutes for them to jot down a slide every few minutes, we lose so much time.
Thank you again for this research and for all of the wonderful resources you provide!
First of all, let me say I really appreciate your blog/podcast. I don’t know where you find the time to research and pull this all together in such a concise and digestible manner. Thank you so much fo all that you do.
Now for some other thoughts. Please know that you are just the first of many educators and presenters who I’ll be commenting on. As educators and presenters, we have to stop using the phrases “THE research shows…” and “Research shows…” It makes us sound authoritative and backed up other authorities but it is disingenuous.
Because “THE research” shows a lot of things. Even in math, medicine, and hard sciences there many disagreements in “THE research”. When my students say, “Research shows…” I always ask “which research?” This forces them to be more direct, honest, and identify the source of their research. I’m not saying you did this but we all are subject to confirmation bias and tend toward research that confirms our view of the world. Some of the studies you cited are several decades old. That alone doesn’t invalidate them but if they haven’t been replicated then we can not make definitive claims about the results. This we now know is true of a LOT of key research in my discipline, psychology. The lack of replication especially with different populations has called into question what we think we KNOW about human nature (or behavior and mental processes).
I think we would all be better off as educators and presenters when we say, “A study by…. backed by studies by….shows….” is far more accurate and genuine in the claims made. In this case, someone else can say, “But didn’t …. show the opposite result and wasn’t there some concern about …’s subject pool or use of xyz statistical method?” This opens us up to the opportunity for a more robust discussion of what “the research shows” and these various results might be applied.
I guess I’m just asking is for us to own our research and references and make it clear where we are getting the information from rather than stating “THE research shows…” This helps the voracity of intellectual debate and discovery as well as advances the inquiry. There’s a tendency to end the discussion when we say, “THE research shows…” as opposed to “According to research by ….”
Thanks again for the work you put in and the products you produce. One more suggestion for note-taking I might suggest is Kwik Notes by Jim Kwik. This technique is fast and simple yet powerful (at least to me) https://jimkwik.com/kwik-brain-013/
Cool site, not been here before. An interesting in depth article I will read in more detail.
Perfecting note taking as an art is essential to me. I find myself writing verbose digital journal entries and porting them over to Anki as a deck is ok but having to modify, break down, refactor the cards takes up half my revision time. I know this is part of encoding but I find my clunky note taking summarisation skills miss the mark and burn productivity time.
My goal is to be able to summarise points I read similar to using the Feynman technique, to be able to convey more with the minimal amount of concise info.
But anyhow thanks for this great resource, will be studying it and further aspect of your site in detail.
How do you recommend adapting these best practices for virtual school? Would you have students take notes digitally so teachers can check them, have students take notes on paper and take pictures of their notes that they upload, or just have students take notes and not have the teacher review them?
Hi Michelle! All of these are viable options, but I think it all depends on the end goal. If you want to see student notes, then I think giving them the choice to type or handwrite is valuable, just like the article mentions. Maybe consider doing this at first to see where students might need some direction and then leave it up to them? For digital notes, there are lots of apps to choose from if that’s a direction you can and want to take. You could check out Microsoft Onenote, something simpler like a shared Google Doc, or Kami if you want your students to annotate a PDF. To submit pictures beyond just emailing them to you, they could be pasted into Google Slides/Powerpoint.
Hi Jennifer – thank you for this. I found this all very helpful when putting together some activities together on note-taking for some new to HE students. Cheers!
I read with interest your document on note taking and the comments that followed. You have provided excellent guidance for a classroom in which is essentially lecture driven as you point out in your first paragraph. In this context notetaking is important because it makes a potentially passive learning environment into an active one, because to take notes, rather than replicating what they see and hear, students must process the experience enough to write it in their own words. By the way, one of the reasons note taking on a computer is less effective for learning is that a good typist can record so quickly that there is no need to think, the information passes from teacher to computer with little processing by the student’s brain. Seen as a learning tool, rewriting and editing notes becomes significant because it creates another opportunity for the student to process and reorganize the information. Thus the advice you provide for taking an editing notes in a lecture context is right on.
However, there is another classroom context in which your suggestions need to be modified. In a classroom where the student is actively engaged by the work itself, as in active reading, or creative math problem solving or science investigations, or any other type of investigation, it is the work itself that engages the student. In this case, notetaking and the notebook take on a different role, and the strategies therefore change and are more nuanced. In this case I prefer to think of the notebook as a grade-level appropriate intellectual diary of the student’s experiences. A format I like has been called by some an interactive notebook in which the right page is a record of the student work and thinking and the left page is a place for further creative thought, perhaps In the form of questions, wonderings, doodles, sketches, etc. In this context, there is no place for editing or rewriting the notes, because the notes represent the most accurate description of what the student experienced because they were written at the time of the experience. Those notes are in a sense sacred since they represent the real experience of the student to the extent that they could represent it. Therefore, they should not be edited. On the other hand, it would be appropriate to create, on subsequent pages, a new document that incorporates information from the notes and other sources to create a more complete explanatory document of the student work.
In this context, the notebook is conceptually divided into two parts, one private, and one public. That distinction plays a role when the teachers evaluates student notebooks. The private part that student creates as work is done is assessed in terms of process and creativity, depending on the context of the lesson plan. If the work is spelled out by the teacher, then the evaluation would be in terms of how well the student used the process provided by the teacher. If the lesson design is more open, the evaluation would be more in terms of what ideas the student brought to the activity. Having done the work and perhaps contributed to a whole class discussion of the work, the student could then write a new entry that includes both their own private notes as well as the insights from other students and the teach in discussion. That public part could then be evaluated on the basis of content accuracy, and if appropriate, writing clarity, accuracy, format, etc.
In the current context in STEM learning, this active classroom format has become the norm but sadly not the most common context, which remains the lecture format. That said, your document is important for those who choose to continue to lecture in spite of the new norms. However, I suggest your document needs to be amended to support those teachers who are working to transition to the new more student centered classroom inherent in the new STEM learning standards.
Hi Joseph! Thank you so much for taking the time to write in and share this. I’ll make sure Jenn sees your suggestions.
The video and article provided many great tips. I want my students to take note taking seriously and not to think of it as a chore. Most of my students take a photo of notes, but I am sure the notes get lost amongst the photos they reall want to view.
Does it improve student “learning” or “retention”? I think there is definitely power in taking notes but does this actually look at deep understanding of a concept and application or retention and regurgitation? Would love to know your thoughts. Thanks for sharing this.
I was listening to this episode while walking on the beach and it hit me that Math Giraffe on TPT offers amazing doodle notes templates. I recently found these and can’t wait to use them in my classroom. I love the research and all the ideas presented.
https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/Graphic-Organizer-Review-Cards-Huge-Deck-of-Bite-Sized-Doodle-Note-Templates-4035675
good info
I always due my notes like this